COPD: Understanding and Managing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. It encompasses conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. With over a decade of experience in this field, I will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and advancements in the management of COPD.
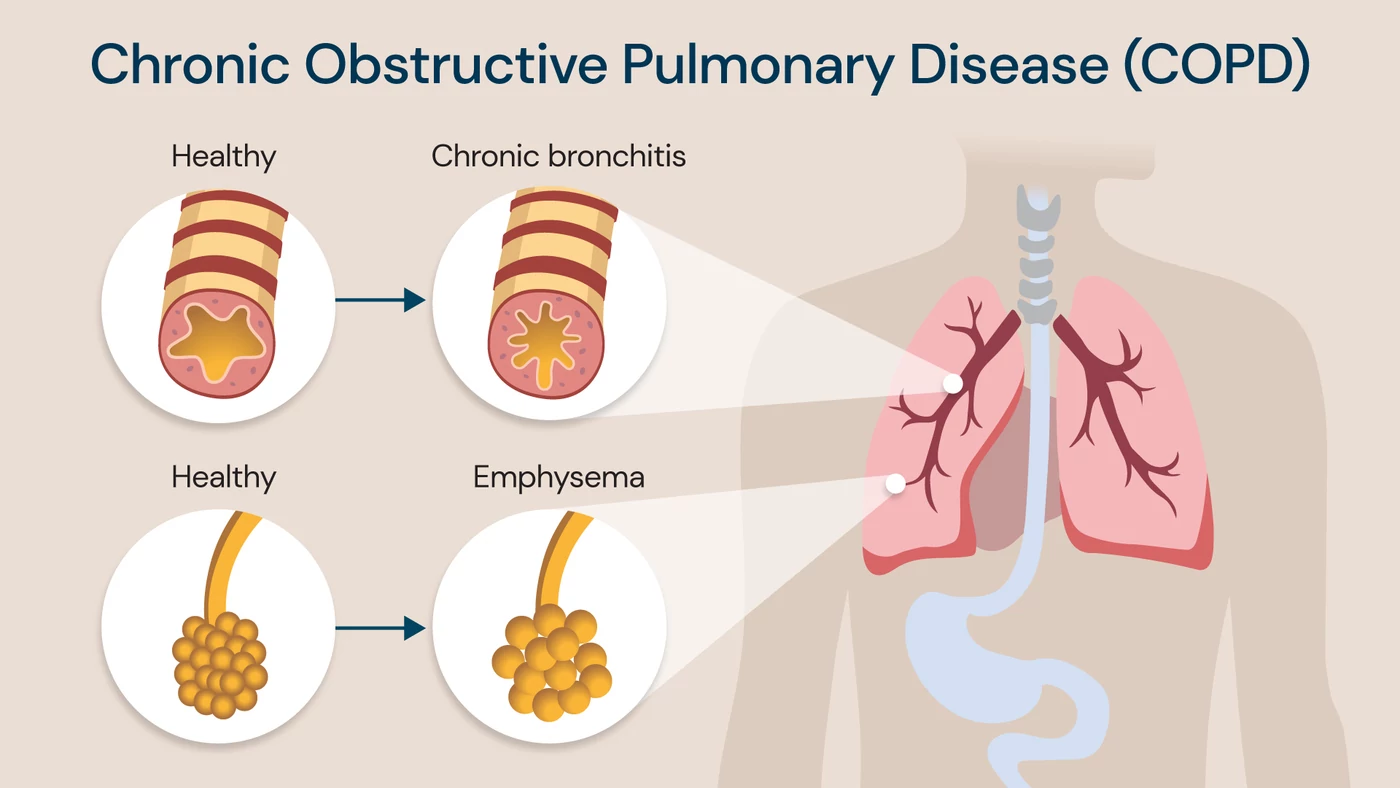
Understanding COPD
COPD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, which leads to airflow obstruction and breathing difficulties. The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways. The most common cause is smoking, but other factors such as air pollution, occupational exposure to dust and chemicals, and genetic factors (such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency) can also contribute to the development of COPD.
Symptoms of COPD
COPD symptoms develop slowly and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Chronic cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Fatigue
- Excess mucus production
Diagnosis of COPD
COPD is diagnosed based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests. Spirometry is the most common test used to diagnose COPD. It measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so, helping to determine the presence and severity of airflow obstruction.
Treatment and Management of COPD
While there is no cure for COPD, treatment can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Management strategies include:
- Medications:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help to relax the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe. They are available in short-acting and long-acting forms.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways and are often used in combination with bronchodilators.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: These oral medications reduce inflammation and relax the airways.
- Antibiotics: These are used to treat respiratory infections that can exacerbate COPD symptoms.
- Oxygen Therapy: For patients with severe COPD and low blood oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen therapy can help improve breathing and quality of life.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This is a comprehensive program that includes exercise training, education, and support to help patients manage their symptoms and improve their physical and emotional well-being.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking is the most important step in managing COPD. Avoiding exposure to lung irritants, eating a healthy diet, and staying active are also crucial.
- Vaccinations: Patients with COPD are at higher risk for respiratory infections. Vaccinations for influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia are recommended to reduce the risk of infections.
Advancements in COPD Treatment
Recent advancements in the treatment of COPD have focused on improving drug delivery, developing new medications, and integrating digital health technologies:
- Triple Therapy Inhalers: These inhalers combine three medications (a long-acting muscarinic antagonist, a long-acting beta-agonist, and an inhaled corticosteroid) in a single device, simplifying treatment regimens and improving patient adherence.
- Biologic Therapies: Research is ongoing to develop biologic therapies that target specific pathways involved in COPD inflammation and progression. These advanced treatments have the potential to provide more personalized and effective management of COPD.
- Smart Inhalers: Smart inhalers equipped with sensors and connectivity features can monitor medication usage, track adherence, and provide real-time feedback to patients and healthcare providers. These devices help ensure correct usage and optimize disease management.
- Telemedicine: The integration of telemedicine in COPD management allows for remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospitalizations.
Conclusion
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a challenging condition that requires ongoing management and care. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, patients can effectively control their COPD and lead a better quality of life. For more information on COPD and related treatments, visit the provided resource.



